Difference between revisions of "2013 Summer Project Week:Fibrosis analysis"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:PW-MIT2013.png|[[2013_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | Image:PW-MIT2013.png|[[2013_Summer_Project_Week#Projects|Projects List]] | ||
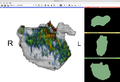
| − | Image: | + | Image:FibrosisPval20130526.png|p-value between DCE-MRI between cured patiens and AFib recurrent patient. |
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
| − | * | + | * Yi Gao, LiangJia Zhu, Josh Cates, Rob MacLeod, Sylvain Bouix, Ron Kikinis, Allen Tannenbaum |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 13: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | + | Among the AFib patients underwent RF ablation, the relative high AFib recurrence rate is a concern. The correlation between the cure/recurrence ratio with the distribution of the fibrosis would provide insight on the disease assessment and treatment planning. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 28: | Line 21: | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
| − | + | The fibrosis distributions on the left atrium wall is imaged using the dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Distributed on different anatomical structures, they are considered as "mass" defined on different domains. Under the framework of the optimal mass transport (OMT), the masses are transported to a common domain where the statistical analysis can then be applied. The significant different regions are then characterized by the low-p-value regions. | |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 28: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | + | * Discussion with Josh about similar work. CARMA has also work on this using particle based shape analysis on surface. This module uses volumetric OMT for the wall volume. | |
| + | * Next | ||
| + | ** validation on particle/OMT based methods | ||
| + | ** Test Extension and then Nightly build | ||
| Line 46: | Line 42: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | * [http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/DBP3:Utah Utah DBP] | ||
| + | * Y Gao, Y Rathi, S Bouix, A Tannenbaum; ''Filtering in the Diffeomorphism Group and the Registration of Point Sets''; IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 21 (10), 4383--4396 | ||
| + | * Y. Gao and S. Bouix, ''Synthesis of realistic subcortical anatomy with known surface deformations''; in MICCAI Workshop on Mesh Processing in Medical Image Analysis, 2012, pp. 80–88. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 21 June 2013
Home < 2013 Summer Project Week:Fibrosis analysis
Key Investigators
- Yi Gao, LiangJia Zhu, Josh Cates, Rob MacLeod, Sylvain Bouix, Ron Kikinis, Allen Tannenbaum
Objective
Among the AFib patients underwent RF ablation, the relative high AFib recurrence rate is a concern. The correlation between the cure/recurrence ratio with the distribution of the fibrosis would provide insight on the disease assessment and treatment planning.
Approach, Plan
The fibrosis distributions on the left atrium wall is imaged using the dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Distributed on different anatomical structures, they are considered as "mass" defined on different domains. Under the framework of the optimal mass transport (OMT), the masses are transported to a common domain where the statistical analysis can then be applied. The significant different regions are then characterized by the low-p-value regions.
Progress
- Discussion with Josh about similar work. CARMA has also work on this using particle based shape analysis on surface. This module uses volumetric OMT for the wall volume.
- Next
- validation on particle/OMT based methods
- Test Extension and then Nightly build
Delivery Mechanism
This work will be delivered to the NA-MIC Kit as a commandline extension.
References
- Utah DBP
- Y Gao, Y Rathi, S Bouix, A Tannenbaum; Filtering in the Diffeomorphism Group and the Registration of Point Sets; IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 21 (10), 4383--4396
- Y. Gao and S. Bouix, Synthesis of realistic subcortical anatomy with known surface deformations; in MICCAI Workshop on Mesh Processing in Medical Image Analysis, 2012, pp. 80–88.