Difference between revisions of "GPU accelerated FEM for simulation and segmentation"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | + | <gallery> | |
Image:PW2009-v3.png|[[2009_Summer_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] | Image:PW2009-v3.png|[[2009_Summer_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] | ||
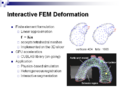
Image:FEM_deform.png|[[FEM deformation]] | Image:FEM_deform.png|[[FEM deformation]] | ||
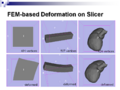
Image:Fem_slicer.png|[[Elastic deformation results on Slicer]] | Image:Fem_slicer.png|[[Elastic deformation results on Slicer]] | ||
| − | + | </gallery> | |
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 25 June 2009
Home < GPU accelerated FEM for simulation and segmentationKey Investigators
- Megumi Nakao and Nobuhiko Hata
Objective
We are developing a fast FEM-based mesh deformation library for interactive simulation and segmentation. The goal in this project week is summarized as
- integrate linear FEM-based deformation algo into the slicer
- perform deformation on specific data
- implement GPU-based acceleration for real-time deformation
Approach, Plan
- integrate a liner FEM solver(original C++ source) into the 3D slicer framework.
- make tetrahedral meshes from medical images and set up physical conditions. Other mesh formats, points and surface models will be probablly accepted.
- evaluate some deformation results qualitatively and improve the simulation.
- try GPU-based acceleration by modifying the linear equation solver using CUBLAS library.
Progress
We have got the following results through this project week
- integrated the FEM-based deformation library into the Slicer framework.
- confirmed elastic deformation results on sample data.
- over 1000 vertices model can be solved in real time using the CUBLAS library.
References
- M. Nakao and K. Minato, "Physics-based Interactive Volume Manipulation for Sharing Surgical Process", IEEE Trans. on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 2009. (To appear)
- H. K. W. Cecilia, M. Nakao and K. Minato, "Automated Volume Sampling Optimization for Direct Volume Manipulation in Patient-specific Surgical Simulation", IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, June 2009. (To appear)
- M. Nakao, S. Yano, T. Matsuyuki, T. Kawamoto and M. Kotaro, "Interactive Volume Manipulation for Supporting Preoperative Planning", Stud. Health Tech. Inform. (MMVR), Vol. 125, pp. 316-321, Jan. 2008.
- M. Nakao, A. Kawashima, K. Minato, M. Kokubo, "Simulating Lung Tumor Motion for Dynamic Tumor-Tracking Irradiation", IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, pp. 4549-4551, Oct. 2007.
- M. Nakao, T. Kuroda, M. Komori, H. Oyama, K. Minato and T. Takahashi, "Transferring Bioelasticity Knowledge through Haptic Interaction", IEEE Multimedia, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp.50-60, Jul. 2006.
- http://kotaro.naist.jp/~meg/eindex.html (My homepage)