Difference between revisions of "Projects:KnowledgeBasedBayesianSegmentation"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
''Data'' | ''Data'' | ||
| − | We are | + | We have applied this algorithm to 20 normal brain MRI data-sets. We used publicly available data-sets from |
| + | the Internet Brain Segmentation Repository (IBSR) offered by the Massachusetts General Hospital, Center for | ||
| + | Morphometric Analysis. The IBSR data-sets are T1-weighted, 3D coronal brain scans after having been | ||
| + | positionally normalized. Manual expert segmentations for these data-sets are publicly available and represent | ||
| + | the ground truth used in this work. | ||
''Algorithm'' | ''Algorithm'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | This algorithm can be cast in either a static or dynamic framework. In the static framework, the following is the algorithm: | ||
# The user sets the number of distinct classes for segmentation: 'N' | # The user sets the number of distinct classes for segmentation: 'N' | ||
| Line 24: | Line 30: | ||
# Smooth the posterior images for 'm' iterations using an affine-invarient anisotropic smoothing filter and renormalize after each iteration (default, m = 5) <br /> | # Smooth the posterior images for 'm' iterations using an affine-invarient anisotropic smoothing filter and renormalize after each iteration (default, m = 5) <br /> | ||
# Apply maximum a posteriori rule to apply labeling and finalize segmentation | # Apply maximum a posteriori rule to apply labeling and finalize segmentation | ||
| + | |||
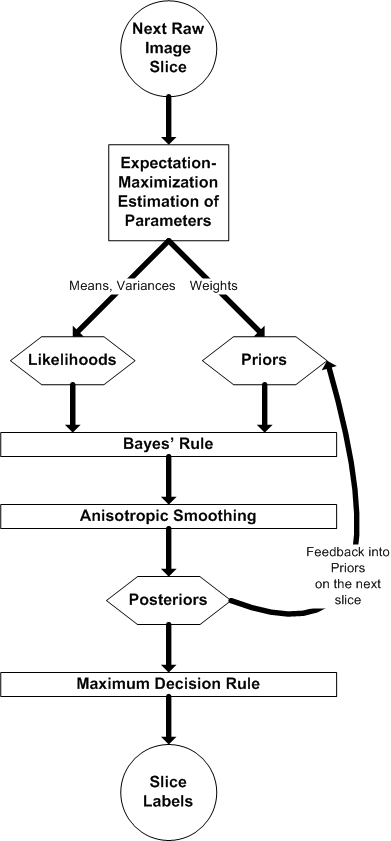
| + | In the dynamic framework, the following image depicts the adaptation of the static framework to the dynamic formulation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Flowchart-classification.png| Dynamic Tissue Tracking Algorithm | center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
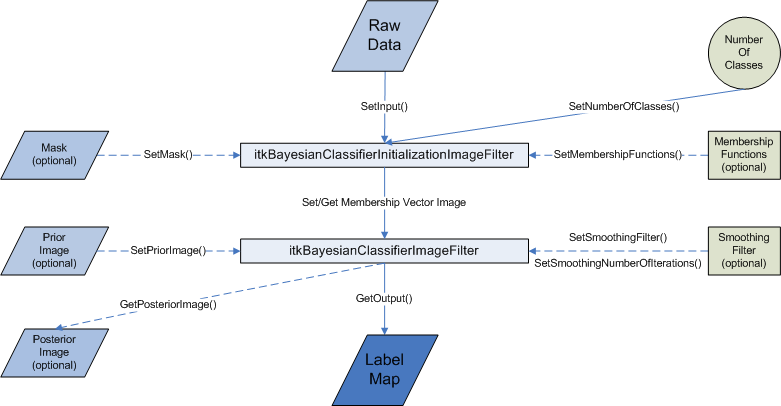
''The ITK filter design'' | ''The ITK filter design'' | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Flowchart.png| Flowchart]] | ||
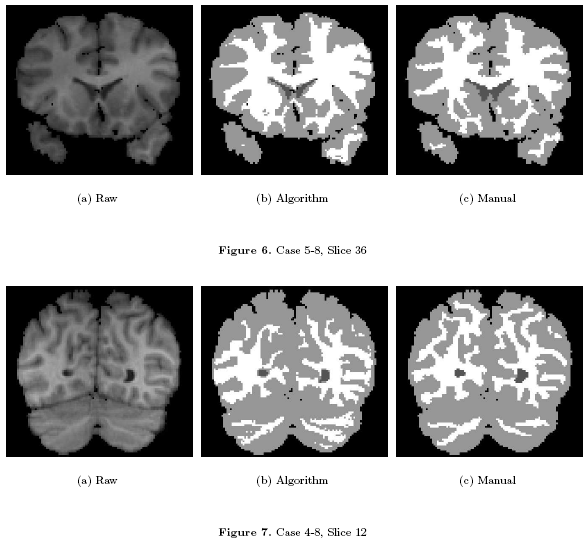
''Some Results'' | ''Some Results'' | ||
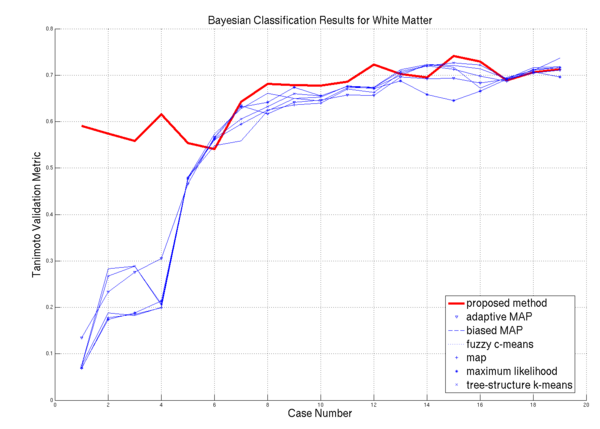
| − | * [[Image: | + | * [[Image:Plot white.png | White Matter Performance on the 20 ISBR datasets | 600px]] WM Algorithm Comparisons |
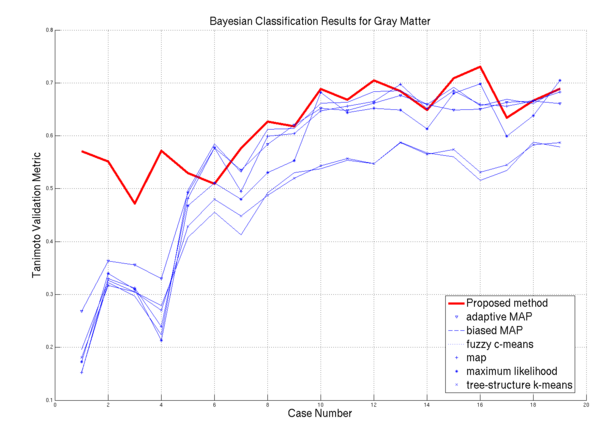
| − | * [[Image: | + | * [[Image:Plot gray.png | Gray Matter Performance on the 20 ISBR datasets | 600px]] GM Algorithm Comparisons |
| − | * [[Image: | + | * [[Image:Fig67.png | Visual Results | 600px]] Visual Results on ISBR data |
''Project Status'' | ''Project Status'' | ||
| Line 43: | Line 57: | ||
''References:'' | ''References:'' | ||
| + | * J. Melonakos, Y. Gao, and A. Tannenbaum. Tissue Tracking: Applications for Brain MRI Classification. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2007. | ||
* J. Melonakos, K. Krishnan, and A. Tannenbaum. An ITK Filter for Bayesian Segmentation: itkBayesianClassifierImageFilter. Insight Journal, 2006. | * J. Melonakos, K. Krishnan, and A. Tannenbaum. An ITK Filter for Bayesian Segmentation: itkBayesianClassifierImageFilter. Insight Journal, 2006. | ||
* J. Melonakos, R. Al-Hakim, J. Fallon, and A. Tannenbaum. Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit. Insight Journal, 2005. | * J. Melonakos, R. Al-Hakim, J. Fallon, and A. Tannenbaum. Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit. Insight Journal, 2005. | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 2 April 2007
Home < Projects:KnowledgeBasedBayesianSegmentationBack to NA-MIC_Collaborations
Objective:
This ITK filter is a segmentation algorithm which utilizes Bayes's Rule along with an affine-invarient anisotropic smoothing filter.
Progress:
Use Case
I'd like to segment a volume or sub-volume into 'N' classes in a very general manner. I will provide the data and the number of classes that I expect and the algorithm will output a labelmap with 'N' classes.
Data
We have applied this algorithm to 20 normal brain MRI data-sets. We used publicly available data-sets from the Internet Brain Segmentation Repository (IBSR) offered by the Massachusetts General Hospital, Center for Morphometric Analysis. The IBSR data-sets are T1-weighted, 3D coronal brain scans after having been positionally normalized. Manual expert segmentations for these data-sets are publicly available and represent the ground truth used in this work.
Algorithm
This algorithm can be cast in either a static or dynamic framework. In the static framework, the following is the algorithm:
- The user sets the number of distinct classes for segmentation: 'N'
- Generate 'N' prior images (default, 'N' uniform prior images)
- Generate 'N' statistical distributions (default, 'N' normal distributions)
- Generate 'N' membership images by applying the statistical distributions to the raw data
- Generate 'N' posterior images by applying Bayes' rule to the prior and membership images
- Smooth the posterior images for 'm' iterations using an affine-invarient anisotropic smoothing filter and renormalize after each iteration (default, m = 5)
- Apply maximum a posteriori rule to apply labeling and finalize segmentation
In the dynamic framework, the following image depicts the adaptation of the static framework to the dynamic formulation:
The ITK filter design
Some Results
Project Status
- Fully incorporated into itkBayesianClassificationImageFilter and itkBayesianClassificationInitializationImageFilter in ITK CVS.
- Fully wrapped in VTK for use in Slicer.
- The working ITK code has been committed to the SandBox
References:
- J. Melonakos, Y. Gao, and A. Tannenbaum. Tissue Tracking: Applications for Brain MRI Classification. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2007.
- J. Melonakos, K. Krishnan, and A. Tannenbaum. An ITK Filter for Bayesian Segmentation: itkBayesianClassifierImageFilter. Insight Journal, 2006.
- J. Melonakos, R. Al-Hakim, J. Fallon, and A. Tannenbaum. Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Brain MRI Scans Using the Insight Toolkit. Insight Journal, 2005.
Key Investigators:
- John Melonakos @ Georgia Tech
- Yi Gao @ Georgia Tech
- Allen Tannenbaum @ Georgia Tech
- Luis Ibanez @ Kitware
- Karthik Krishnan @ Kitware
Links: