Difference between revisions of "NA-MIC-Kit"
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | | style="width:10%" | [[Image: | + | | style="width:10%" | [[Image:3DSlicerLogo-V-Color-201x204.png|thumb|left|200px]] |
| style="width:90%" | | | style="width:90%" | | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. [[NA-MIC-Kit-Tools:Slicer|More...]] | To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. [[NA-MIC-Kit-Tools:Slicer|More...]] | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 62: | Line 61: | ||
To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. [[NA-MIC-Kit-Tools:Slicer|More...]] | To represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. [[NA-MIC-Kit-Tools:Slicer|More...]] | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 4 October 2007
Home < NA-MIC-Kit
| |||||
Contents
Overview
The NA-MIC Kit consists of open source software with application in biomedical computing. This software has been and continues to be produced by the NA-MIC team as part of an NIH National Center for Biomedical Computing program. The software is distributed under a BSD-style, open source license free of commercial and reciprocal distribution restrictions. See this presentation on the NA-MIC Kit for more information.
Target Audience
The NA-MIC Kit has been created to support a spectrum of users and developers. This includes:
- biomedical researchers
- algorithms developers
- application developers
- software toolkit developers and users; and
- software process tools including support for building, testing, community building and software management.
The NA-MIC Kit has also been employed by users wishing to perform image analysis and visualization tasks. For example, the Slicer application is being used at | Harvard's IIC for astrophysics research. Other tools, such as CMake, are in wide use around the world in projects as disparate as KDE, one of the world's open source software projects distributed as the Linux desktop windowing environment.
Software Overview
Depending on user needs, users of the NAMIC Kit will use the following software tools. More information about each tool is available below.
- 3D Slicer is a general purpose application. Biomedical researchers will typically use this software tool to load, view, analyze, process and save data.
- Slicer modules, which are dynamically loaded by Slicer at run-time, can be used to extend Slicer's core functionality including defining graphical user interfaces. Modules are typically used by algorithms and application developers.
- Application and algorithms developers may also use NA-MIC Kit toolkits and libraries. For example, the Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit ITK can be used to develop slicer modules for medical image analysis. The Visualization Toolkit can be used to process and visualize data. KWWidgets is a 2D graphical user interface toolset that can be used to build applications. Teem is a library of general purpose command-line tools that are useful for processing data. Finally, those individuals wishing to create
Download Central
Please go here to download software, documentation and data.
Software Packages
Go to NA-MIC-Kit-Old to see the previous NA-MIC Kit web pages.
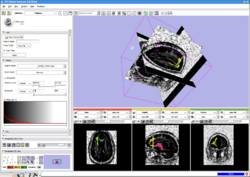
3D SlicerTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More...
| |
The Visualization Toolkit VTKTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More...
| |
The Insight Toolkit ITKTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. | |
KWKidgets GUI ToolkitTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. | |
Teem Command Line ToolsTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. | |
CMake The Cross-platform Make ToolTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. |