Difference between revisions of "2011 Summer Project Week Quantitative Magnetic Susceptibility Mapping"
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {| | |
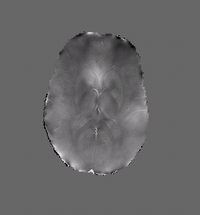
| − | + | |[[File:PD susc est ppm1.png|thumb|200 px|Susceptibility Map 1]] | |
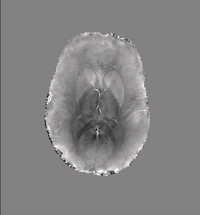
| + | |[[File:PD susc est ppm2.png|thumb|200 px|Susceptibility Map 2]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| Line 8: | Line 11: | ||
'''Full Title of Project''' | '''Full Title of Project''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quantitative Magnetic Susceptibility Mapping | ||
==Key Investigators== | ==Key Investigators== | ||
| − | * | + | * MIT: Clare Poynton |
| − | * UCLA: | + | * BWH: Sandy Wells |
| + | * UCLA: Andrei Irimia | ||
| Line 19: | Line 25: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
| − | + | Quantifying magnetic susceptibility in the brain from the phase of the MR signal provides a non-invasive means for measuring the | |
| − | + | accumulation of iron believed to occur with aging and neurodegenerative disease. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | We describe a variational approach to susceptibility estimation that incorporates a tissue-air atlas to resolve ambiguity | |
| + | in the susceptibility estimates, while eliminating additional biasfields through application of the Laplacian. | ||
| + | Results show improved correlation with postmortem iron concentrations relative to competing methods. | ||
| + | The goal for this week is to apply this method to evaluate magnetic susceptibility of lesions associated with TBI. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 41: | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
Our plan for the project week: | Our plan for the project week: | ||
| − | + | * Discuss applications with collaborators and try to refine the algorithm | |
| − | * Discuss with collaborators and try to refine the algorithm | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 49: | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | + | * Algorithm: Improved background field correction, resulting in improved mean susceptibility values: | |
| + | Thalamus ( -0.06 ppm ) | ||
| + | Caudate (0.02 ppm) | ||
| + | Putamen (0.05 ppm) | ||
| + | Globus Pallidus (0.11 ppm) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Applications: Obtained 3 TBI cases from DBP 3, which we are currently analyzing | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 64: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:44, 24 June 2011
Home < 2011 Summer Project Week Quantitative Magnetic Susceptibility Mapping
Full Title of Project
Quantitative Magnetic Susceptibility Mapping
Key Investigators
- MIT: Clare Poynton
- BWH: Sandy Wells
- UCLA: Andrei Irimia
Objective
Quantifying magnetic susceptibility in the brain from the phase of the MR signal provides a non-invasive means for measuring the accumulation of iron believed to occur with aging and neurodegenerative disease.
We describe a variational approach to susceptibility estimation that incorporates a tissue-air atlas to resolve ambiguity in the susceptibility estimates, while eliminating additional biasfields through application of the Laplacian.
Results show improved correlation with postmortem iron concentrations relative to competing methods.
The goal for this week is to apply this method to evaluate magnetic susceptibility of lesions associated with TBI.
Approach, Plan
Our plan for the project week:
- Discuss applications with collaborators and try to refine the algorithm
Progress
- Algorithm: Improved background field correction, resulting in improved mean susceptibility values:
Thalamus ( -0.06 ppm ) Caudate (0.02 ppm) Putamen (0.05 ppm) Globus Pallidus (0.11 ppm)
- Applications: Obtained 3 TBI cases from DBP 3, which we are currently analyzing