AAPM 2013
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < AAPM 2013

| ||||

|

|

|

|

|
Introduction
3D Slicer, is a free, open source software package for visualization and image analysis. 3D Slicer is natively designed to be available on multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux and Mac OS X.
The goal of the user group meeting is to bring together current and prospective 3D Slicer users and developers to discuss of 3D Slicer's present and future as a software application for therapy and imaging.
Logistics
- Date: Monday, August 5, 2013
- Time: 12:30PM-2:00PM
- Location: JW Marriott, Room 304 Third Floor
Organizers
- Gregory Sharp, Nadya Shusharina, Justin Phillips, MGH
Program
- 12:45-1:00 Presentation: "3D Slicer version 4.2 -> 4.3", Greg Sharp
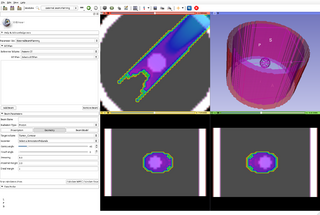
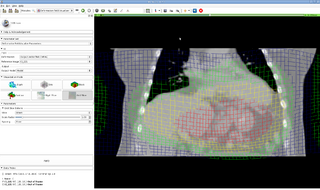
- 1:00-1:15 Live demo: "Proton dose calculations", Justin Phillips
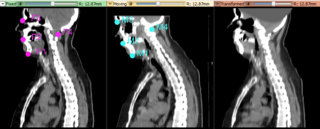
- 1:15-1:30 Live demo: "Interactive B-spline registration with landmark constraints", Nadya Shusharina
- 1:30-1:45 Group discussion
Registration
Registration is not required. All are invited.
Meeting Minutes
The audience provided valuable feedback about their
Training
- Documentation still out of date
- Google hangout, may not work at all locations
- Developer documentation for python is sadly lacking
Bug and feature requests (infrastructure)
- Better DICOM-RT support sorely needed, esp export & import
- External beam planning module would be good to use with external dose engines
- Can't read DICOM because extra files in the same folder
- Loading DICOM is slow
- Matlab bridge is difficult to get working
- Sets of 2D images are not handled well
Bug and feature requests (registration)
- Reg-2-3 hard to build
- Improved automatic rigid registration
- Qualitative evaluation of deformable registration, such as shared cursor or split screen
- ROI for registration
- Intensity-based range of values for registration
- Mass-preservising registration