Difference between revisions of "2009 Winter Project Week StochasticTractography"
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|[[Image:NAMIC-SLC.jpg|thumb|320px|Return to [[2009_Winter_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] ]] | |[[Image:NAMIC-SLC.jpg|thumb|320px|Return to [[2009_Winter_Project_Week|Project Week Main Page]] ]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:St_helix_test_01_GUI.png|thumb|320px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
===Key Investigators=== | ===Key Investigators=== | ||
| − | * BWH: Marek Kubicki, Julien | + | * BWH: Marek Kubicki, Julien de Siebenthal |
<div style="margin: 20px;"> | <div style="margin: 20px;"> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
<h1>Objective</h1> | <h1>Objective</h1> | ||
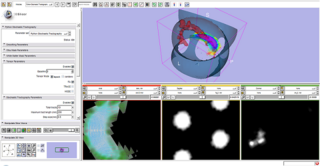
| − | + | Stochastic Tractography module has the ultimate goal to offer an estimation of the probability of white matter connection between two regions of the brain. For that, connectivity map is the fundamental output of the current algorythm implementation. It reveals given two regions the distribution of probability of connection per voxel. | |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
<h1>Approach, Plan</h1> | <h1>Approach, Plan</h1> | ||
| − | + | A complete pipeline implementation was forseen in order to give to the researcher the best access to the different features Stochastic Tractography can offer. Based on the MatLAB implementation and constantly compared to it, a Python integration was devised. It offers as a proof of concept the possibility to directly prototype an algorithm with direct integration into the Slicer solution without using MatLAB. This should alleviate issues related to code translation from MatLAB to Slicer. | |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
<h1>Progress</h1> | <h1>Progress</h1> | ||
| − | + | The pipeline is implemented and functional. First test series show accurate adequacy between MatLAB and Python numerical computations of the Stochastic Tractography algorythm. We would like during NAMIC integrate already existing Python wrapping of the Rician and Eddy current correction filters. An ideal wrapping solution for Slicer is indeed still to be defined. Moreover, we would like also during NAMIC to find out an EPI correction filter or if needed prototype a new one. | |
Latest revision as of 16:51, 16 December 2008
Home < 2009 Winter Project Week StochasticTractography Return to Project Week Main Page |
Key Investigators
- BWH: Marek Kubicki, Julien de Siebenthal
Objective
Stochastic Tractography module has the ultimate goal to offer an estimation of the probability of white matter connection between two regions of the brain. For that, connectivity map is the fundamental output of the current algorythm implementation. It reveals given two regions the distribution of probability of connection per voxel.
Approach, Plan
A complete pipeline implementation was forseen in order to give to the researcher the best access to the different features Stochastic Tractography can offer. Based on the MatLAB implementation and constantly compared to it, a Python integration was devised. It offers as a proof of concept the possibility to directly prototype an algorithm with direct integration into the Slicer solution without using MatLAB. This should alleviate issues related to code translation from MatLAB to Slicer.
Progress
The pipeline is implemented and functional. First test series show accurate adequacy between MatLAB and Python numerical computations of the Stochastic Tractography algorythm. We would like during NAMIC integrate already existing Python wrapping of the Rician and Eddy current correction filters. An ideal wrapping solution for Slicer is indeed still to be defined. Moreover, we would like also during NAMIC to find out an EPI correction filter or if needed prototype a new one.
References
- Björnemo M, Brun A, Kikinis R, Westin CF. Regularized stochastic white matter tractography using diffusion tensor MRI. In Fifth International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI'02). Tokyo, Japan, 2002;435-442.
- Friman, O., Farneback, G., Westin CF. A Bayesian Approach for Stochastic White Matter Tractography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Vol 25, No. 8, Aug. 2006
- Shenton, M.E., Ngo, T., Rosenberger, G., Westin, C.F., Levitt, J.J., McCarley, R.W., Kubicki, M. Study of Thalamo-Cortical White Matter Fiber Tract Projections in Schizophrenia Using Diffusion Stochastic Tractography. Poster presented at the 46th Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, Boca Raton, FL, December 2007.