DBP3:Utah:RegSegPipeline
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < DBP3:Utah:RegSegPipeline
back to DBP3 home
Contents
The CARMA DBP: MRI-based study and treatment of atrial fibrillation
Alex Zaitsev, Dominik Meier, Ron Kikinis
Pilot Studies on a Registration & Segmentation Pipeline & Workflow
Main processing pipeline
- N4 bias field correction for the MRI (surface coils):
- run on entire image gives some benefit that may be improved with masking: again the dominant intensity dropoff from the surface coil occurs along the chest wall and ribcage. Even if that is not the structure of interest, it is the low-freq. variation the bias correction algorithm is searching for, and masking that out can be counter-productive: via masking we may end up with a smoother image, but the intensity variations removed were not caused by the coil but are actually true signal.
- Module used: N4 ITK; Parameters: convergence: 1e-5, iterations: 50,40,30,20, shrink factor: 3
- registration MRA>cMRI
- the MRA contains the same FOV and has surrounding structures (liver, chest, spine etc) visible also, despite lower intensities. A global affine is thus not necessarily going to benefit from masking the heart, unless the relative motion of the heart becomes the dominant reason for misalignment.
- Module used: BRAINSfit
- tried masking with both BrainsFit and RobustMultires modules. Both failed to provide better alignment with masking.
- images have good alignment to begin with, need reliable fiducial to evaluate registration. E..g. descending aorta? non-cardiac structures?
- registration follow-up -> baseline
- most reliably done on the post contrast MRI.
- DOF at least 12, because image is captured at different phases in the breathing/cardiac cycle, some low-res BSpline should be beneficial
- Module used: BRAINSfit
- the IS FOV can differ, e.g. how much of the liver is included. If the two exams differ significantly (>30%) in that content, a prior cropping step is suggested to better match image content before registration. Resampling to isotropic voxel size at this stage is also advantageous.
- ROI definition (manual box ROI or automated via atlas)
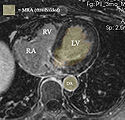
- segmentation of LA from MRA -> inner wall
- as a dynamic image the MRA contains significant spread and likely requires interactive segmentation/thresholding to yield a satisfactory LA volume
- Module used: Editor: thresholding or thresholding within Volumes thresholding option within Display tab, use iron colormap & low alpha setting to check for ventricular wall borders.
- cropping and island removal
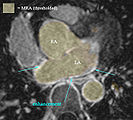
- LA wall segmentation
- very small structure, most reliably done manually direct. Starting with automation may yield more effort on post-edits
- Module used: Editor: manual outline
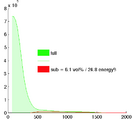
- segmentation of enhancement within LA wall: intensity statistics. An atlas-based set of intensity distributions may be more meaningful here than a simple Otsu, because both amount and location of enhancement is unknown and can in theory be 0.
Example Cases
- Example Case P2 : pre-post registration
- This example contains significant MRI (motion?) artifacts that require dedicated processing to isolate the structures of interest
- E.g. FOV includes much more of liver on pre exam, which needs to be cropped to amount matching the follow-up