Difference between revisions of "MeningiomaMRIRegistrationStudy"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
===FSL FLIRT=== | ===FSL FLIRT=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/flirt/index.html FSL FLIRT] | ||
| + | * [http://www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/research/flirt/ Technical details] | ||
| + | * parameters: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | flirt -in ${TIME_POINT_2} -ref ${TIME_POINT_1} -omat ${FLIRT_TRANSFORM} -out ${RESAMPLED_IMAGE} -dof 6 -v | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * execution time: ~4 min | ||
==Parameter exploration== | ==Parameter exploration== | ||
Revision as of 15:54, 20 July 2009
Home < MeningiomaMRIRegistrationStudyContents
Objective
Accurate registration of same patient/same modality MRI data for longitudinal analysis of tumor progression.
Specific Aims
- Compare the accuracy of registration using existing Slicer and non-Slicer tools
- Identify parameter settings that produce satisfactory results
- Outline the limitations of the available registration tools in the context of the specific clinical research application
Data
- Input images: isotropic post-contrast T1 MRI acquired at different locations of BWH during 2006-2008, used under medical records study IRB. Time period between acquisition of scans for each patient is about 1 year.
- Ground truth transformation: not available
- Expert landmarks for registration evaluation: not available
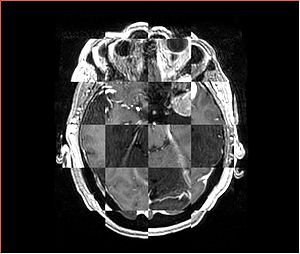
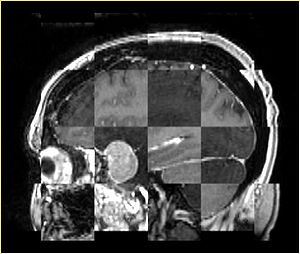
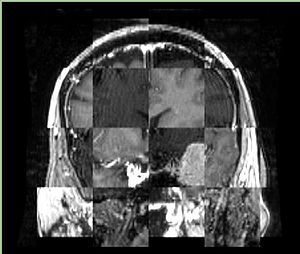
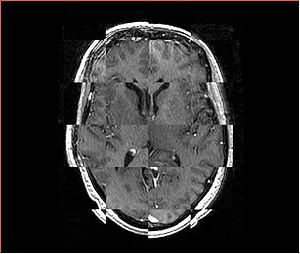
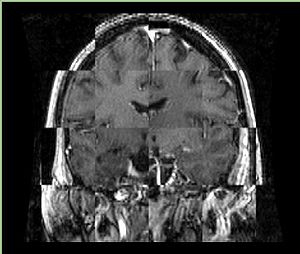
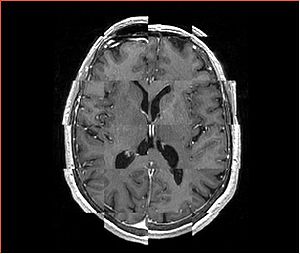
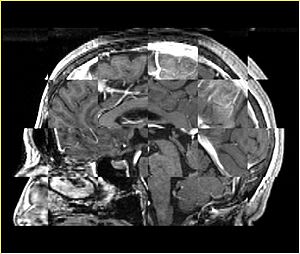
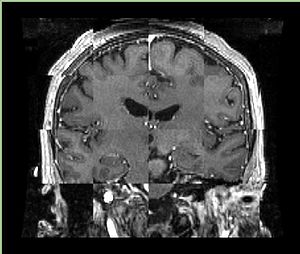
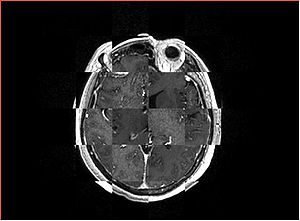
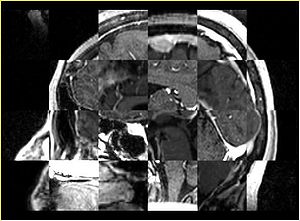
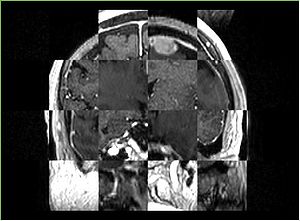
- Checkerboard appearance of unregistered images for the representative data of interest
- Case01
- Case03
- Case04
- Case10
Measures of success
- qualitative assessment: visually pleasing results
- quantitative assessment: something better than "visually pleasing" (TBD)
- minimum execution time to meet the application requirements: interactive quantification of tumor growth
Methods
Registration
RegisterImages Slicer module
RigidRegistration Slicer module
BRAINSFit
FSL FLIRT
- FSL FLIRT
- Technical details
- parameters:
flirt -in ${TIME_POINT_2} -ref ${TIME_POINT_1} -omat ${FLIRT_TRANSFORM} -out ${RESAMPLED_IMAGE} -dof 6 -v
- execution time: ~4 min