Difference between revisions of "Projects:RegistrationDocumentation:UseCaseInventoryNotes"
From NAMIC Wiki
(Created page with '* <span style="color: rgb(50, 180, 0);">List of cases collected/inventoried thus far is here:</span> 150px|right|108 Level Tree …') |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:UseCaseHierarchySnapshot_108Levels.png|150px|right|108 Level Tree]] | [[Image:UseCaseHierarchySnapshot_108Levels.png|150px|right|108 Level Tree]] | ||
[[Image:UseCaseHierarchySnapshot_360Levels.png|150px|right|360 Level Tree]] | [[Image:UseCaseHierarchySnapshot_360Levels.png|150px|right|360 Level Tree]] | ||
| − | * | + | *The registration case library will contain the most common scenarios encountered for Slicer Registration. Each case will contain a dataset, a parameter set, a guided tutorial with example result. The hierarchy will be represented graphically as a tree and as a list with links to the abovementioned data. The library will be as exhaustive as possible, containin brain and non-brain, different modalities (MRI, CT, PET/SPECT). |
*considered is also a list of troubleshooting cases, i.e. a list of the most common sources of registration failure, again complete with dataset, tutorial and remedy. | *considered is also a list of troubleshooting cases, i.e. a list of the most common sources of registration failure, again complete with dataset, tutorial and remedy. | ||
*the organization of a use case hierarchy can be accomplished in several ways. The main categories are listed below. Not all combinations exist or are equally common occurrences. For example, a different-timepoint/contrast distinction is not necessary for inter-subject registration. | *the organization of a use case hierarchy can be accomplished in several ways. The main categories are listed below. Not all combinations exist or are equally common occurrences. For example, a different-timepoint/contrast distinction is not necessary for inter-subject registration. | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 10 November 2009
Home < Projects:RegistrationDocumentation:UseCaseInventoryNotes- List of cases collected/inventoried thus far is here:
- The registration case library will contain the most common scenarios encountered for Slicer Registration. Each case will contain a dataset, a parameter set, a guided tutorial with example result. The hierarchy will be represented graphically as a tree and as a list with links to the abovementioned data. The library will be as exhaustive as possible, containin brain and non-brain, different modalities (MRI, CT, PET/SPECT).
- considered is also a list of troubleshooting cases, i.e. a list of the most common sources of registration failure, again complete with dataset, tutorial and remedy.
- the organization of a use case hierarchy can be accomplished in several ways. The main categories are listed below. Not all combinations exist or are equally common occurrences. For example, a different-timepoint/contrast distinction is not necessary for inter-subject registration.
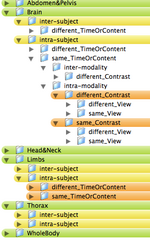
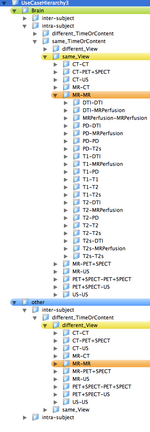
- ORGAN: Brain, Head&Neck, Thorax, Abdomen&Pelvis, Limbs, WholeBody
- SUBJECT: intra-subject, inter-subject
- MODALITY: intra-modality, inter-modality
- CONTRAST: same_Contrast, different_Contrast
- MR, CT, PET+SPECT, US
- T1, T2, PD, T2s, DTI, MRPerfusion
- CONTENT: same_TimeOrContent, different_TimeOrContent
- VIEW: same_View, different_View
- Depending on grouping this leads to trees with 80-1080 entries. Two example hierarchies (directory trees) are here: 108 Level Tree , 360 Level Tree
- the VIEW distinction arises from commonly occurring problems of co-registering sets acquired with different slice orientation. The basics of dealing with axis orientation is already integrated into the algorithm, but further details remain: basically different_view implies a possibly high voxel size ratio (i.e. different voxel sizes if one image acquired axial the other coronal). Actions/Parameter settings are with multi-resolution settings, blurring and special checking of the axis orientation (vox2ras) meta-data. If, for example,voxel size ratio is close to [1 1 1] we need not do anything different other than resample based on vox2ras.
- No separate distinction for Atlas Registration, i.e. the case where the volume of interest is not the one used for calculating the transform.
- User-populated content The exploding # of combinations makes a successful top-down approach difficult. More effective to organize bottom-up, i.e. have user invited content, which we organize into a growing tree. We can make a call to the user community for submitting datasets and registration problems. This call should be in the "Register Images" Documentation as well as the "Help&Acknowledgement" tab of the "Register Images" module. e.g. Post a link on the documentation pages and module info tabs: Having trouble with registration? Try our service. We will consider all cases, provided that you have already tried what we do offer on the library and that did not work. If it didn't then that speaks for having your case added.
"if you have an interesting registration problem that is not yet covered in our library, send us your case: we will post it along with our best registration solution/strategy. If you agree to the posting of the anonymized image data, you get a free registration, the user community gets a new example case. Everybody wins."