Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C01
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C01
Back to ARRA main page
Back to Registration main page
Back to Registration Use-case Inventory
Contents
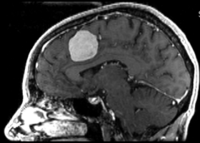
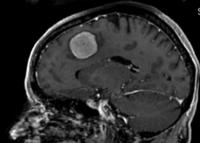
Slicer Registration Use Case Exampe #2: Inter-subject Brain MRI: axial T1 Tumor Growth AssessmentI
Objective / Background
This is a classic case of change assessment. We want to know if the tumor changed since last exam.
Keywords
MRI, brain, head, intra-subject, T1, tumor growth, meningioma, change assessment
Input Data
 reference/fixed : T1 SPGR , 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.4 mm voxel size, axial, RAS orientation.
reference/fixed : T1 SPGR , 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.4 mm voxel size, axial, RAS orientation. moving: T1 SPGR , 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.2 mm voxel size, sagittal, RAS orientation.
moving: T1 SPGR , 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.2 mm voxel size, sagittal, RAS orientation.- Content preview: Have a quick look before downloading: Does your data look like this? Media:RegUC2_lightbox.png
- download dataset to load into slicer (~17 MB zip archive)
Registration Challenges
- accuracy is the critical criterion here. We need the registration error (residual misalignment) to be smaller than the change we want to measure.
- we have slightly different voxel sizes
- if the pathology change is substantial it might affect the registration.
- the different series may have different FOV.
- the different series may have different resolution / voxel sizes.
Key Strategies
- the SPGR is the anatomical reference. It is also higher resolution. Unless there are overriding reasons, always use the highest resolution image as your fixed/reference.
- the defacing of the SPGR image introduces sharp edges that can be detrimental. Best to mask that area. If you have the mask available, use it. But in this case since we already have a skull-stripping mask as part of the labelmap, that is even better. We will load the labelmap and use it as mask in finding the registration
- because the two images are still reasonably similar in contrast, we can choose an intensity ratio as cost function, which is less stable but if successful provides a more precise alignment than mutual information.
Procedures
- download registration parameter presets file (load into slicer and run the registration)
- download/view guided video tutorial
- download power point tutorial
- download step-by step text instructions (text only)
Registration Results
- result transform file (load into slicer and apply to the target volume)
- result screenshots (compare with your results)
- result evaluations (metrics)