Difference between revisions of "Projects:longitudinaldwi"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
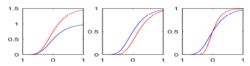
| − | |[[Image:Gompertz.PNG|thumb|250px|Effects | + | |[[Image:Gompertz.PNG|thumb|250px|Effects on varying the three parameters asymptote, delay, and rate of change of Gompertz growth function.]] |
|[[Image:Gompertz-FCT.PNG|thumb|250px|Gompertz Growth Function.]] | |[[Image:Gompertz-FCT.PNG|thumb|250px|Gompertz Growth Function.]] | ||
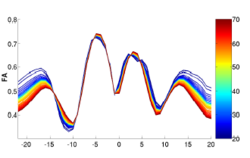
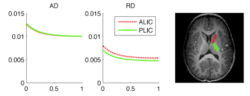
|[[Image:ALIC-PLIC.PNG|thumb|250px|Example: Growth of axial and transversal diffusivity (AD, RD) from birth to 2 years of the anterior and posterior left internal capsule (ALIC, PLIC) in early infant study.]] | |[[Image:ALIC-PLIC.PNG|thumb|250px|Example: Growth of axial and transversal diffusivity (AD, RD) from birth to 2 years of the anterior and posterior left internal capsule (ALIC, PLIC) in early infant study.]] | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 11 April 2011
Home < Projects:longitudinaldwiContents
Longitudinal Analysis of DWI image data
Description
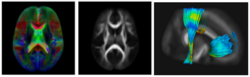
Subject-specific analysis of image data often includes comparison of follow-up to baseline, or serial staging of progress of disease or for monitoring therapeutic intervention. Key methodological components are intra-subject registration of the set of scans, and analysis of geometric deformations and appearance changes. In DWI data, such analysis includes deformation of the set of DWI with associated correction of tensor orientation or local ODF adjustement. In addition, scalar invariants such as FA, MD, axial and radial diffusivities have to be compared in regions or along tracts at corresponding anatomical locations.
The availability of longitudinal or serial 3D image data for each subject, the image processing gets new opportunities for spatio-temporal processing of 4D datasets. The conventional cross-sectional comparison between subjects are groups at various time points is replaced by comparison and analysis of subject-specific change trajectories. In this project, we focus on the development of longitudinal analysis of DTI.
Constrained Data Decomposition and Regression for Longitudinal Fiber Tract Diffusion
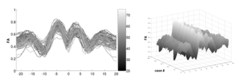
We have developed a methodology based on constrained PCA (CPCA) for fitting age-related changes of white matter diffusion of fiber tracts. CPCA is applied to a functional data analysis (FDA) problem, where diffusion along parametrized fiber tracts, e.g. FA or MD, represent functions of arc-length. Age regression on tract functions reveals a nonlinear trajectory but also age-related changes varying locally along tracts.
Sylvain Gouttard, Marcel Prastawa, Elizabeth Bullitt, Casey Goodlett and Guido Gerig, Constrained Data Decomposition and Regression for Analyzing Healthy Aging from Fiber Tract Diffusion Properties, Springer LNCS 5761, Proc. MICCAI’09, pp. 321-328, 2009
Statistical Growth Modeling of Longitudinal DT-MRI
This research presents a framework to model growth trajectories and to determine significant regional differences in growth pattern characteristics, applied to longitudinal neuroimaging data. We use nonlinear mixed effect modeling where temporal change is modeled by the Gompertz function. The Gompertz function uses intuitive parameters related to delay, rate of change, and expected asymptotic value; all descriptive measures which can answer clinical questions related to growth. Our proposed framework combines nonlinear modeling of individual trajectories, population analysis, and testing for regional differences. We will apply this framework to longitudinal DTI studies of NA-MIC DBP partners, which include acute/follow-up DTI in TBI and serial DTI in the Huntington Diseases PREDICT project, where thee time-points will be available.
N. Sadeghi, M. Prastawa, J. H. Gilmore, W. Lin, and G. Gerig, "Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Early Brain Development," in Proceedings IEEE Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Nov. 2010, in print
Application to longitudinal DTI in Huntington Disease
to come soon
Key Investigators
- Utah: Anuja Sharma, Sylvain Gouttard, Guido Gerig
- IOWA: Hans Johnson