Difference between revisions of "AHM2009:Mind"
Hjbockholt (talk | contribs) |
Hjbockholt (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
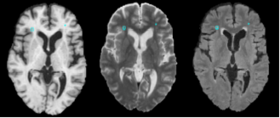
**The pipeline attempts to solve the problem of segmenting white matter lusions in lupus. The capability is aimed at clinical researchers. | **The pipeline attempts to solve the problem of segmenting white matter lusions in lupus. The capability is aimed at clinical researchers. | ||
| − | * How does the pipeline compare to state of the art | + | * How does the pipeline compare to state of the art? |
| − | **The state of the art is a work in progress in N-SLE. There are many approaches that attempt to solve lesion classification in Multiple Sclerosis. Some of these approaches are automated or semi-automated; however, all automatic approaches suffer a lack of | + | **The state of the art is a work in progress in N-SLE. There are many approaches that attempt to solve lesion classification in Multiple Sclerosis (where it is much more common to perform neuroimaging studies). Some of these approaches are automated or semi-automated; however, all automatic approaches suffer a lack of ground truth. It is difficult for humans manual raters to agree on fuzzy boundaries across different image constrasts (e.g., T1, T2, FLAIR). |
| − | A good example of the | + | A good example of the challenge that remains in terms of lesion segmentation was the the 2008 MICCAI Conference [http://www.ia.unc.edu/MSseg/ MS Lesion Segmentation Challenge] this past May in the form of a grant challenge in segmentation. Several groups, including this DBP, competed by first being providing training data-sets with two manual labellings, approaches were judged on an application set naive to each classification approach. |
==Detailed Information about the Pipeline== | ==Detailed Information about the Pipeline== | ||
Revision as of 06:09, 8 January 2009
Home < AHM2009:Mind
MIND Roadmap Project
Overview
- What problem does the pipeline solve, and who is the targeted user?
- The pipeline attempts to solve the problem of segmenting white matter lusions in lupus. The capability is aimed at clinical researchers.
- How does the pipeline compare to state of the art?
- The state of the art is a work in progress in N-SLE. There are many approaches that attempt to solve lesion classification in Multiple Sclerosis (where it is much more common to perform neuroimaging studies). Some of these approaches are automated or semi-automated; however, all automatic approaches suffer a lack of ground truth. It is difficult for humans manual raters to agree on fuzzy boundaries across different image constrasts (e.g., T1, T2, FLAIR).
A good example of the challenge that remains in terms of lesion segmentation was the the 2008 MICCAI Conference MS Lesion Segmentation Challenge this past May in the form of a grant challenge in segmentation. Several groups, including this DBP, competed by first being providing training data-sets with two manual labellings, approaches were judged on an application set naive to each classification approach.
Detailed Information about the Pipeline
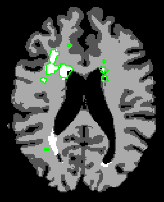
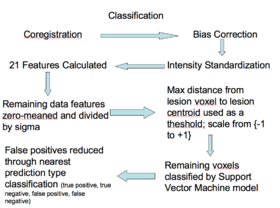
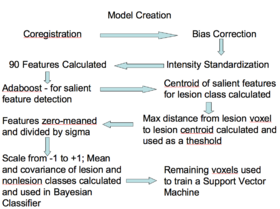
- Illustrate the components and workflow of the pipeline using your own data
- Training
- Approximately 90 features were computed based on the T1, T2, and FLAIR, including neighborhood means with varying radii, mathematical morphometry dilation and erosion, kmeans clustering, and gradients, among others
- Adaboost was applied to the data to find the 20 features that best discriminate lesion from non-lesion
- Those 20 features were then calculated for all lesions, for all subjects, then zero-meaned and the standard deviation was set to one.
- The centroid of the lesions was then calculated and the max distance found between the centroid and the lesion voxels
- The max distance threshold was used to exclude voxels that had no chance of being lesions
- The features for all voxels within the distance threshold were calculated and scaled to a range of negative one to positive one
- The means and covariance of these features were calculated for both the lesion and non-lesion classes and used to define the two classes in a Bayesian classifier
- A parameter search was then performed to find the prior that gave the best combination of Specificity and Sensitivity.
- Classifying
- The 20 relevant features are calculated, zero-meaned and sigma set to one, thresholded based on the distance to the lesion centroid, and then passed to the Bayesian classifier
- Training
- Demonstrate parameters/steps that need to be adjusted using someone else's data
Software & documentation
- We have a very active project for this pipeline on the NITRC resource 3DSlicerLupusLesionModule
Team
- DBP: Affiliation & logo
- Core 1: Affiliation & logo
- Core 2: Affiliation & logo
- Contact: H. Jeremy Bockholt, hjbockholt@mrn.org
Outreach
- Publication Links to the PubDB.
- H. J. Bockholt, V. A. Magnotta, M. Scully, C. Gasparovic, B. Davis, K. Pohl, R. Whitaker, S. Pieper, C. Roldan, R. Jung, R. Hayek, W. Sibbitt, J. Sharrar, P. Pellegrino, R. Kikinis. A novel automated method for classification of white matter lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Presented at the 38th annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience, Washingto, DC, 15 – 19 November 2008
- Scully M., Magnotta V., Gasparovic C., Pelligrimo P., Feis D., Bockholt H.J. 3D Segmentation In The Clinic: A Grand Challenge II at MICCAI 2008 - MS Lesion Segmentation. IJ - 2008 MICCAI Workshop - MS Lesion Segmentation. Available http://grand-challenge2008.bigr.nl/proceedings/pdfs/msls08/282_Scully.pdf
- 2008 SFN conference outreach activity
- 2009 AAN conference outreach activity
References
Adaboost and Support Vector Machines for White Matter Lesion Segmentation in MR Images. Quddus A, Fieguth P, Basir O. PAMI Lab, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005;1:463-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17282216
Architecture for an Artificial Immune System Steven A. Hofmeyr, Stephanie Forrest Evolutionary Computation Winter 2000, Vol. 8, No. 4, Pages 443-473 http://www.mitpressjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1162/106365600568257
Automated segmentation of white matter lesions in 3D brain MR images, using multivariate pattern classification Zhiqiang Lao; Dinggang Shen; Jawad, A.; Karacali, B.; Dengfeng Liu; Melhem, E.R.; Bryan, R.N.; Davatzikos, C. Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro, 2006. 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Volume , Issue , 6-9 April 2006 Page(s): 307 - 310 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/login.jsp?url=/iel5/10818/34114/01624914.pdf?temp=x
Automatic Segmentation of MS Lesions Using a Contextual Model for the MICCAI Grand Challenge Jonathan H. Morra, Zhuowen Tu, Arthur W. Toga, Paul M. Thompson IJ - 2008 MICCAI Workshop - MS Lesion Segmentation http://www.midasjournal.org/browse/publication/280