Difference between revisions of "2014 Summer Project Week:Atlas Selection"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<h3>Objective</h3> | <h3>Objective</h3> | ||
Atlas selection is used for image segmentation. Normally, a single image is chosen as an atlas and the structures are segmented manually. | Atlas selection is used for image segmentation. Normally, a single image is chosen as an atlas and the structures are segmented manually. | ||
| − | The segmentation is transferred to patient data using non-linear image registration. However, image segmentation based on single atlas is | + | The segmentation is transferred to patient data using non-linear image registration. However, image segmentation based on single image atlas is |
| − | not stable. To improve the segmentation we can select multiple images, which are suitable for image segmentation and after registration we | + | not stable. To improve the segmentation, we can select multiple images, which are suitable for image segmentation and after registration we |
| − | can merge the segmentations to a final one. | + | can merge the segmentations to a final one. An idea to improve the atlas selection process is that we take advantage of using an average atlas. |
| + | The procedure of atlas selection used for image segmentation is defined as follows: | ||
* Construct an atlas based on a database | * Construct an atlas based on a database | ||
| − | * Every image of the database is aligned to the atlas after atlas construction | + | * Every image of the database is aligned to the atlas after the average atlas construction. |
| − | * Register the atlas to a new image and transfer the database to the new image | + | * Register the average atlas to a new image and transfer the database and their segmentations to the new image. |
| − | * Compare the transformed database | + | * Compare the transformed database with the new image in the ROI and select some well-matched images with respected to some distance measure, e.g. MI, CC, NGF. |
| − | * Merge the segmentations of these images to a final one based on e.g. | + | * Merge the segmentations of these well-matched images to a final one based on e.g. weighted voting or STAPLE algorithm. |
| − | The crucial step of atlas selection is atlas construction | + | The crucial step of atlas selection is the average atlas construction. The focus of this project lies on the construction of an average atlas using 3D datasets and validate the average atlas with the inspection of segmentations. |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | ||
<h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | <h3>Approach, Plan</h3> | ||
| − | + | The average atlas construction modeling and algorithm are based on non-linear image registration and reconstruction. | |
| − | + | The algorithm does not depend on selecting a particular image as the template and the solution is optimal with respect to a minimization problem. | |
| + | In this project we want to construct an atlas using a database with segmentations and validate the average atlas by the visual inspection of merged segmentations. | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | <div style="width: 27%; float: left; padding-right: 3%;"> | ||
<h3>Progress</h3> | <h3>Progress</h3> | ||
| − | * We developed algorithms for atlas construction, programming in Matlab and visualization in Slicer. | + | * We developed algorithms for the average atlas construction, finished programming in Matlab. and visualization in Slicer. |
| − | * We constructed | + | * We constructed the average atlas of 20 datasets for H&N and merged segmentations into the average atlas. |
| + | * We visualized the average atlas and its probability maps of segmentations in the Slicer. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 20:15, 26 June 2014
Home < 2014 Summer Project Week:Atlas SelectionKey Investigators
- Kanglin Chen (Fraunhofer MEVIS Germany)
- Gregory Sharp (Harvard Medical School)
Project Description
Objective
Atlas selection is used for image segmentation. Normally, a single image is chosen as an atlas and the structures are segmented manually. The segmentation is transferred to patient data using non-linear image registration. However, image segmentation based on single image atlas is not stable. To improve the segmentation, we can select multiple images, which are suitable for image segmentation and after registration we can merge the segmentations to a final one. An idea to improve the atlas selection process is that we take advantage of using an average atlas. The procedure of atlas selection used for image segmentation is defined as follows:
- Construct an atlas based on a database
- Every image of the database is aligned to the atlas after the average atlas construction.
- Register the average atlas to a new image and transfer the database and their segmentations to the new image.
- Compare the transformed database with the new image in the ROI and select some well-matched images with respected to some distance measure, e.g. MI, CC, NGF.
- Merge the segmentations of these well-matched images to a final one based on e.g. weighted voting or STAPLE algorithm.
The crucial step of atlas selection is the average atlas construction. The focus of this project lies on the construction of an average atlas using 3D datasets and validate the average atlas with the inspection of segmentations.
Approach, Plan
The average atlas construction modeling and algorithm are based on non-linear image registration and reconstruction. The algorithm does not depend on selecting a particular image as the template and the solution is optimal with respect to a minimization problem. In this project we want to construct an atlas using a database with segmentations and validate the average atlas by the visual inspection of merged segmentations.
Progress
- We developed algorithms for the average atlas construction, finished programming in Matlab. and visualization in Slicer.
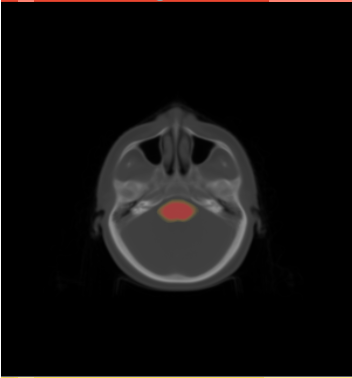
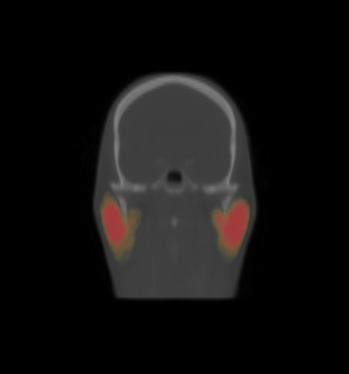
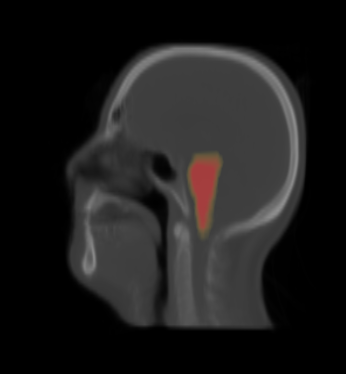
- We constructed the average atlas of 20 datasets for H&N and merged segmentations into the average atlas.
- We visualized the average atlas and its probability maps of segmentations in the Slicer.
Project Results
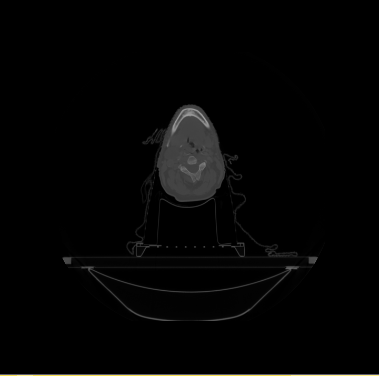
- We have 20 datasets for H&N including lung and chest. For example
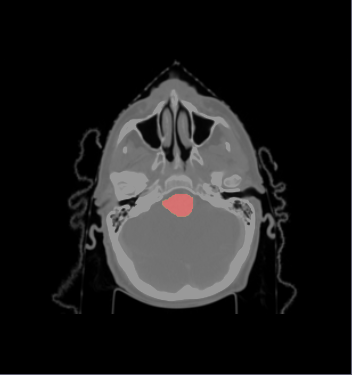
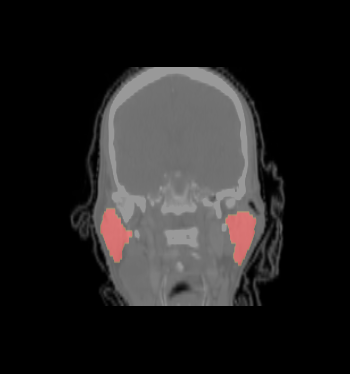
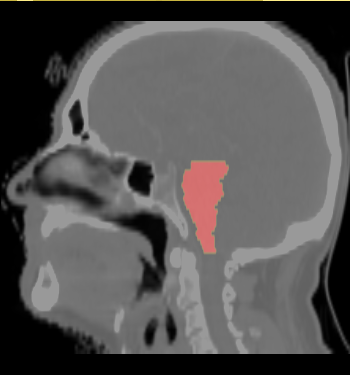
- We select the ROI of every data excluding lung and chest. For each data there exist the segmentations of brain stem, left and right parotids. For example
- We constructed an atlas from 20 datasets of ROI, and merged the segmentations. These segmentations are probability maps of
brain stem, left and right parotids.