Difference between revisions of "NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:New"
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
<font color="red">'''New: '''</font> D. Nain, M. Styner, M. Niethammer, J. J. Levitt, M E Shenton, G Gerig, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. Statistical Shape Analysis of Brain Structures using Spherical Wavelets. Accepted in The Fourth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI ’07) that will be held April 12-15, 2007 in Metro Washington DC, USA. | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> D. Nain, M. Styner, M. Niethammer, J. J. Levitt, M E Shenton, G Gerig, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. Statistical Shape Analysis of Brain Structures using Spherical Wavelets. Accepted in The Fourth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI ’07) that will be held April 12-15, 2007 in Metro Washington DC, USA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | [[Image:Progress_Registration_Segmentation_Shape.jpg|200px]] | ||
| + | | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == [[Projects:ShapeBasedSegmentationAndRegistration|Shape Based Segmentation and Registration]] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This type of algorithm assigns a tissue type to each voxel in the volume. Incorporating prior shape information biases the label assignment towards contiguous regions that are consistent with the shape model. [[Projects:ShapeBasedSegmentationAndRegistration|More...]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> K.M. Pohl, J. Fisher, S. Bouix, M. Shenton, R. W. McCarley, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells. Using the Logarithm of Odds to Define a Vector Space on Probabilistic Atlases. Medical Image Analysis,11(6), pp. 465-477, 2007. <b>Best Paper Award MICCAI 2006 </b> | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 21:02, 22 December 2007
Home < NA-MIC Internal Collaborations:NewBack to NA-MIC Collaborations
Diffusion Image Analysis
Fiber Tract Extraction and Analysis
|
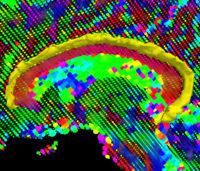
Geodesic Tractography SegmentationIn this work, we provide an energy minimization framework which allows one to find fiber tracts and volumetric fiber bundles in brain diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI). More... New: J. Melonakos, E. Pichon, S. Angenet, and A. Tannenbaum. Finsler Active Contours. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007. |
Fractional Anisotropy Analysis
Path of Interest Analysis
Validation
Algorithm/Software Infrastructure
Structural Image Analysis
Image Segmentation
|
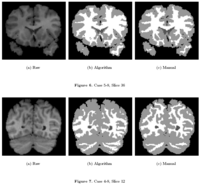
Knowledge-Based Bayesian SegmentationThis ITK filter is a segmentation algorithm that utilizes Bayes's Rule along with an affine-invariant anisotropic smoothing filter. More... New: J. Melonakos, Y. Gao, and A. Tannenbaum. Tissue Tracking: Applications for Brain MRI Classification. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2007. |
|
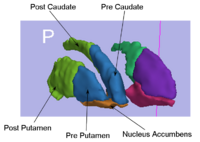
Rule-Based Striatum SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the striatum. More... New: Al-Hakim, et al. Parcellation of the Striatum. SPIE MI 2007. |
|
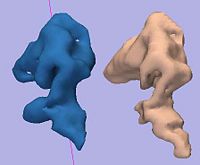
Rule-Based DLPFC SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. More... New: Al-Hakim, et al. A Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Semi-Automatic Segmenter. SPIE MI 2006. |
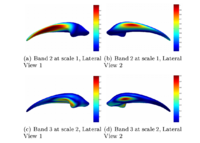
|
Multiscale Shape Segmentation TechniquesTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... New: Delphine Nain won the best student paper at MICCAI 2006 in the category "Segmentation and Registration" for her paper entitled "Shape-driven surface segmentation using spherical wavelets" by D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. |
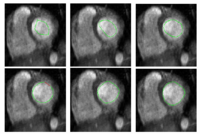
|
Stochastic Methods for SegmentationNew stochastic methods for implementing curvature driven flows for various medical tasks such as segmentation. More... New: Currently under investigation. |

|
Statistical/PDE Methods using Fast Marching for SegmentationThis Fast Marching based flow was added to Slicer 2. More... |
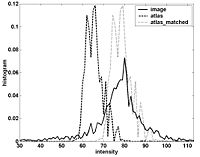
|
Atlas Renormalization for Improved Brain MR Image Segmentation across Scanner PlatformsAtlas-based approaches have demonstrated the ability to automatically identify detailed brain structures from 3-D magnetic resonance (MR) brain images. Unfortunately, the accuracy of this type of method often degrades when processing data acquired on a different scanner platform or pulse sequence than the data used for the atlas training. In this paper, we improve the performance of an atlas-based whole brain segmentation method by introducing an intensity renormalization procedure that automatically adjusts the prior atlas intensity model to new input data. Validation using manually labeled test datasets has shown that the new procedure improves the segmentation accuracy (as measured by the Dice coefficient) by 10% or more for several structures including hippocampus, amygdala, caudate, and pallidum. The results verify that this new procedure reduces the sensitivity of the whole brain segmentation method to changes in scanner platforms and improves its accuracy and robustness, which can thus facilitate multicenter or multisite neuroanatomical imaging studies. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |
Image Registration

|
Optimal Mass Transport RegistrationThe goal of this project is to implement a computationaly efficient Elastic/Non-rigid Registration algorithm based on the Monge-Kantorovich theory of optimal mass transport for 3D Medical Imagery. Our technique is based on Multigrid and Multiresolution techniques. This method is particularly useful because it is parameter free and utilizes all of the grayscale data in the image pairs in a symmetric fashion and no landmarks need to be specified for correspondence. More... New: Tauseef ur Rehman, A. Tannenbaum. Multigrid Optimal Mass Transport for Image Registration and Morphing. SPIE Conference on Computational Imaging V, Jan 2007. |
Morphometric Measures and Shape Analysis
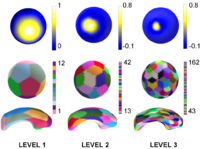
|
Multiscale Shape AnalysisWe present a novel method of statistical surface-based morphometry based on the use of non-parametric permutation tests and a spherical wavelet (SWC) shape representation. More... New: D. Nain, M. Styner, M. Niethammer, J. J. Levitt, M E Shenton, G Gerig, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum. Statistical Shape Analysis of Brain Structures using Spherical Wavelets. Accepted in The Fourth IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI ’07) that will be held April 12-15, 2007 in Metro Washington DC, USA. |
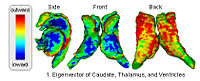
|
Shape Based Segmentation and RegistrationThis type of algorithm assigns a tissue type to each voxel in the volume. Incorporating prior shape information biases the label assignment towards contiguous regions that are consistent with the shape model. More... New: K.M. Pohl, J. Fisher, S. Bouix, M. Shenton, R. W. McCarley, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells. Using the Logarithm of Odds to Define a Vector Space on Probabilistic Atlases. Medical Image Analysis,11(6), pp. 465-477, 2007. Best Paper Award MICCAI 2006 |

|
Spherical WaveletsCortical Surface Shape Analysis Based on Spherical Wavelets. We introduce the use of over-complete spherical wavelets for shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces. Bi-orthogonal spherical wavelets have been proved to be powerful tools in the segmentation and shape analysis of 2D closed surfaces, but unfortunately they suffer from aliasing problems and are therefore not invariant to rotation of the underlying surface parameterization. In this paper, we demonstrate the theoretical advantage of over-complete wavelets over bi-orthogonal wavelets and illustrate their utility on both synthetic and real data. In particular, we show that the over-complete spherical wavelet transform enjoys significant advantages for the analysis of cortical folding development in a newborn dataset. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 |
Topology CorrectionGeometrically-Accurate Topology-Correction of Cortical Surfaces using Non-Separating Loops. We propose a technique to accurately correct the spherical topology of cortical surfaces. Specifically,we construct a mapping from the original surface onto the sphere to detect topological defects as minimal nonhomeomorphic regions. The topology of each defect is then corrected by opening and sealing the surface along a set of nonseparating loops that are selected in a Bayesian framework. The proposed method is a wholly self-contained topology correction algorithm, which determines geometrically accurate, topologically correct solutions based on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) intensity profile and the expected local curvature. Applied to real data, our method provides topological corrections similar to those made by a trained operator. More... New: IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 26, NO. 4, APRIL 2007 | |
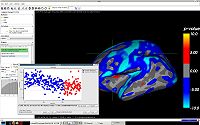
|
QDEC: An easy to use GUI for group morphometry studiesQdec is a application included in the Freesurfer software package intended to aid researchers in performing inter-subject / group averaging and inference on the morphometry data (cortical surface and volume) produced by the Freesurfer processing stream. The functionality in Qdec is also available as a processing module within Slicer3, and XNAT. More... See: Qdec user page |
fMRI Analysis
Functional Activation Analysis
Algorithm and Software Infrastructure

|
Conformal FlatteningThe goal of this project is for better visualizing and computation of neural activity from fMRI brain imagery. Also, with this technique, shapes can be mapped to shperes for shape analysis, registration or other purposes. Our technique is based on conformal mappings which map genus-zero surface: in fmri case cortical or other surfaces, onto a sphere in an angle preserving manner. More... New: Y. Gao, J. Melonakos, and A. Tannenbaum. Conformal Flattening ITK Filter. ISC/NA-MIC Workshop on Open Science at MICCAI 2006. |
NA-MIC Kit
NAMIC Software Process
Software Infrastructure
Training & Dissemination
Other Projects

|
Numerical Recipies ReplacementOur objective is to replace algorithms using the proprietary Numerical Recipes for C source base in FreeSurfer in the efforts to open-source FreeSurfer. This project has been completed through the use of the open source packages VXL (VNL) and Cephes. This includes the complete replacement of all Numerical Recipes in C code, and the implementation of a battery of unit tests for each replaced function. Currently the open source release is at a beta stage, and 25 beta releases of the source have been made. We anticipate a complete open source release in first quarter 2008. More... New: Completed |