Difference between revisions of "2010 Winter Project Week Musco Skeletal Segmentation"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<i><u>Approach:</u></i> | <i><u>Approach:</u></i> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| − | Objective 1: We have adopted a multi-contrast MR methodology to segment knee bones and cartilage structures. The algorithm utilizes tissue intensity information from multiple MR contrasts to segment structures of interest. Inputs to the algorithm included n registered MR image sets. The algorithm created an n-dimensional space of voxel intensities associated with the n image sets. The user assigned seed points to the structures of interest, and the algorithm created a cluster center for each structure of interest. Cluster radii were calculated based on standard deviations obtained from seed points, and tissue structures classified | + | Objective 1: We have adopted a multi-contrast MR methodology to segment knee bones and cartilage structures. The algorithm utilizes tissue intensity information from multiple MR contrasts to segment structures of interest. Inputs to the algorithm included n registered MR image sets. The algorithm created an n-dimensional space of voxel intensities associated with the n image sets. The user assigned seed points to the structures of interest, and the algorithm created a cluster center for each structure of interest. Cluster radii were calculated based on standard deviations obtained from seed points, and tissue structures were classified as label maps. |
| − | + | For more details, please visit http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/Stanford_Simbios_group | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | For | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 43: | ||
<i><u>Plan: </u></i> | <i><u>Plan: </u></i> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| − | a. | + | a. Incorporate a method to clean label maps (remove undesired bridge connections). |
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| − | b. | + | b. Implement an algorithm to extract smoothed boundaries from label maps. |
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 01:20, 4 January 2010
Home < 2010 Winter Project Week Musco Skeletal Segmentation
Key Investigators
- Stanford: Harish Doddi, Saikat Pal, Scott Delp
- Kitware: Luis Ibanez
Objective
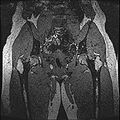
The aim of this project is to develop a methodology for rapid segmentation of knee structures from magnetic resonance (MR) images for subject-specific modeling. The overall goal can be broken down into two specific objectives -
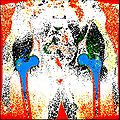
1. Rapid segmentation of target structures into label maps.
2. Generation of simulation-ready models from existing atlas and label maps of individual structures.
Approach, Plan
Approach:
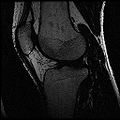
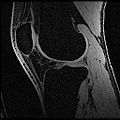
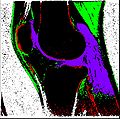
Objective 1: We have adopted a multi-contrast MR methodology to segment knee bones and cartilage structures. The algorithm utilizes tissue intensity information from multiple MR contrasts to segment structures of interest. Inputs to the algorithm included n registered MR image sets. The algorithm created an n-dimensional space of voxel intensities associated with the n image sets. The user assigned seed points to the structures of interest, and the algorithm created a cluster center for each structure of interest. Cluster radii were calculated based on standard deviations obtained from seed points, and tissue structures were classified as label maps.
For more details, please visit http://www.na-mic.org/Wiki/index.php/Stanford_Simbios_group
Plan:
a. Incorporate a method to clean label maps (remove undesired bridge connections).
b. Implement an algorithm to extract smoothed boundaries from label maps.
Progress
Finished segmenting different regions of interest like bones, cartilage etc.
Created label maps from existing segmented output.